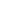Curettage of Periodontal Pockets
Periodontal pocket curettage is a modern method for treating periodontal disease lesions. It provides mechanical cleansing of the affected areas from granulation tissue and bacteria. Come to ID Dent for curettage!
| Duration of procedure | 1-2 visits |
| Procedure length | 30-60 minutes |
| Contraindications | Infections, hemophilia |
| Types of curettage | Open, closed |
| Post-procedure care | Avoid hard foods, smoking, and drinking |
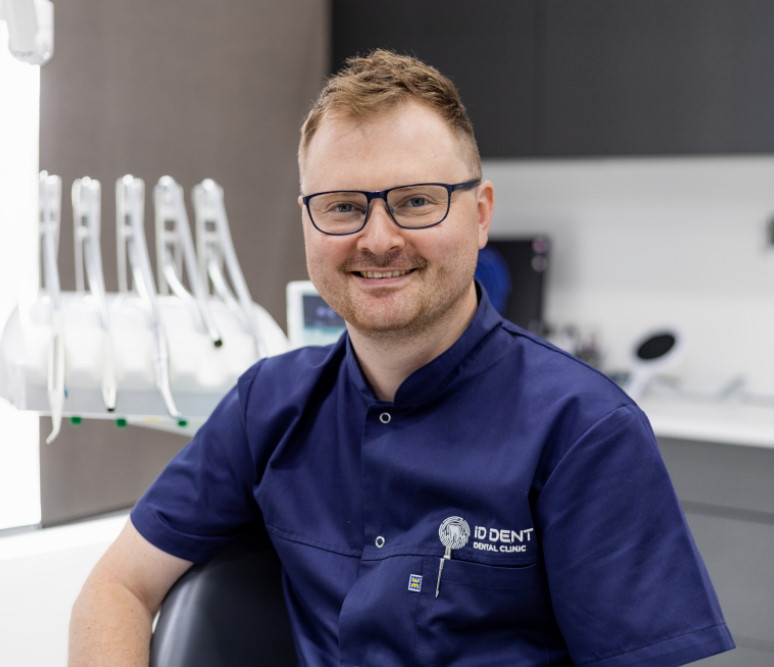

Periodontal pocket curettage is a mechanical cleaning of the tooth root surface from granulation tissue, bacteria, and tartar. Main indications for curettage include blood and pus discharge from periodontal pockets and pocket depths exceeding 3 mm. The... Read more
Periodontal pocket curettage is a mechanical cleaning of the tooth root surface from granulation tissue, bacteria, and tartar. Main indications for curettage include blood and pus discharge from periodontal pockets and pocket depths exceeding 3 mm. The procedure is a dentist’s decision after thorough oral diagnostics.
At ID Dent in Kyiv’s Lesnoy district, quality tooth and gum treatment is assured. We conduct periodontal pocket curettage painlessly, swiftly, and effectively, offering affordable treatment prices. We look forward to your consultation!

Swelling, bleeding, and tenderness of the gums can severely affect your quality of life. Eating and cleaning your teeth become challenging. In the worst cases, the problem leads to tooth mobility. But don’t worry: the dentists at ID Dent in Kyiv know how to restore the health of your gums! To treat complex oral diseases, we perform periodontal pocket curettage. This medical procedure helps remove plaque and inflamed tissue. Your gums will be healthy again, and your smile — stunning!
Curettage, from the English word “curettage,” means scraping, i.e., removing pathological granulations and treating the tooth root surface to encourage new epithelial attachment.
What is a periodontal pocket?
A periodontal pocket is a pathological formation in the tissues surrounding the teeth. It occurs due to inflammatory processes in the gum and periodontal tissues, especially if the inflammation is chronic.
The formation of a periodontal pocket creates a favorable environment for bacterial accumulation, further damaging periodontal tissues and worsening without medical help.
Consequences of periodontal damage
Plaque and tartar accumulated in the periodontal pocket provide a favorable environment for bacterial growth. This can lead to acute or chronic periodontitis. In the worst case, periodontitis can result in bone tissue destruction around the tooth and tooth loss.
In addition to periodontitis, periodontal damage may result in other diseases such as gingivostomatitis and periodontal disease. These cause gum bleeding and swelling, tooth pain, and can lead to tooth loosening and loss.
Additionally, periodontal illnesses influence overall health. Many studies link periodontal disease to heart disease, strokes, diabetes, and other illnesses.
This is why regular dentist visits for check-ups and professional tooth cleaning are important. If periodontal disease is detected, immediate professional intervention is advised.
Treatment depends on the damage level and can include periodontal pocket curettage, medication, surgery, or a combination of methods.
Causes of plaque formation in periodontal pockets
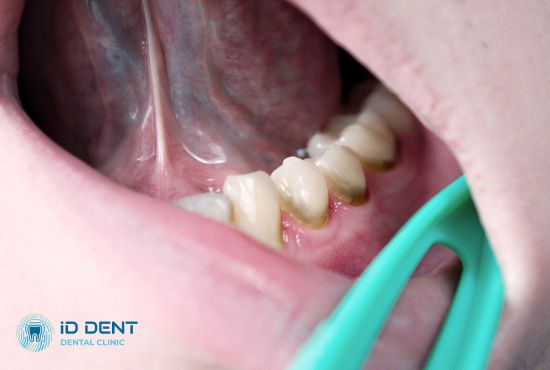
Major causes of plaque include improper oral care and dietary issues. Bacteria and deposits can accumulate on uncleaned tooth surfaces and then enter the periodontal pocket.
Dietary imbalances can also cause plaque. High sugar, fatty, and processed food intake can disrupt oral microflora, leading to a high plaque and tartar appearance rate.
Additional plaque causes:
- Taking certain medications.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Ignored professional hygiene; regular dentist visits are a must if prone to gum diseases.
Indications for gum curettage
Periodontal pocket curettage in Kyiv is a medical procedure performed by a periodontist to remove plaque and inflamed tissue from periodontal pockets. It is currently the most effective periodontitis treatment method.
The main indication for curettage is a periodontal pocket depth exceeding 3 mm. Other cleaning indications include bleeding gums, pus discharge, frequent periodontitis, and ineffective treatments.
Contraindications
Curettage isn’t performed if the patient has:
- Infectious diseases.
- Hemophilia and thrombocytopenia.
- Acute cardiovascular diseases.
Curettage is also delayed during pregnancy and lactation.
A pre-procedure dental consultation for risk and complication discussion is required.
Types of curettage
There are two main procedure types:
- Open curettage.
- Closed curettage.
The method is chosen based on pocket depth and individual clinical features.
Closed Curettage
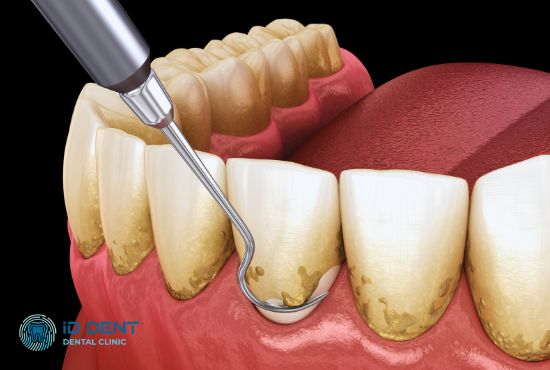
Closed periodontal pocket curettage is a dental procedure for treating shallow gum-tooth gaps. Main indications include mild or moderate periodontitis, lack of bone formations in pockets, and dense gum structure.
The procedure begins with mouth rinsing with an antiseptic. Then, near the tooth, the gum is treated with a numbing gel. Special dental tools — scalers and curettes — scrape off supra- and subgingival soft and hard deposits. All tooth row surfaces with inflamed periodontal pockets are treated. Granulation tissue is removed with curettes. Pocket cavities are disinfected, and healing ointments are applied under the gum.
Post-procedure, the dentist advises on home treatment and care.
Open Curettage
Open periodontal pocket curettage is a dental procedure where the dentist accesses the tooth root and pockets to clean them of plaque and bacteria. It is performed for significantly deep periodontal pockets.
Open curettage can involve local anesthesia or general anesthesia (depends on case complexity). Typically, it’s done on 1-2 teeth in 30-60 minutes.
Procedure Process
If you consult a dentist for periodontal disease, proceed as follows:
- Conduct diagnostics for disease evaluation and precise diagnosis.
- Develop a treatment plan.
- Select curettage type based on clinical picture.
- Administer anesthesia and perform curettage.
After the procedure, the dentist advises on home care and prescribes medications.
Rehabilitation Period
Post-procedure, follow guidelines to avoid complications and aid tooth and gum health recovery.
Initial days post-curettage may involve mild pain and discomfort. Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics are prescribed for infection prevention and healing acceleration. Rest, avoid physical and thermal stress, and use prescribed medications, such as antiseptics, anti-inflammatories, antibiotics, are crucial.
Oral care post-gum pocket curettage
Post-procedure, ensure you:
- Brush teeth at least twice daily with a soft brush. Be cautious to avoid gum injury.
- Use mouthwash to remove remnants that may cause infection.
- Avoid hard foods and fried products for several days. Opt for soft foods and drink water instead.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol for several days. This speeds healing and prevents infection.
Gum Curettage Cost in Kyiv by ID Dent
The cost of periodontal pocket curettage varies greatly due to factors like disease type and form and patient specifics. At ID Dent, we prioritize delivering quality, affordable treatment. Costs depend on factors such as cleaning-required tooth quantity and pocket depth. Approximate prices are available on our site, but for accurate information and consultation, contact us.
If you have gum issues, visit ID Dent. Our experienced doctors use modern equipment for oral disease diagnostics and treatment, offering high-quality care and tailored treatment.
Located on Kyiv’s left bank, Lesnoy district, the ID Dent clinic is easily accessible for all Kyiv residents, by car or public transport. Nearby are Lesnaya and Chernigovskaya metro stations.
Don’t delay oral health care, contact us for quality consultation and gum problem treatment. We are ready to assist you at any time!
Literature list:
- Roger Detienne. Advanced Periodontitis Treatment. Azbuka. – 2008. – 120 pages.
- Shtorina G.B., Karaeva A.Yu. Preparation and performance of surgical interventions for generalized periodontitis. Man – 2014. – 152 pages.
- Borisenko A.V. Periodontal diseases. Medicine. – 2013.

 Kyiv, st. Bratislavskaya 14B
Kyiv, st. Bratislavskaya 14B Mon.-Fri. 9-20, Sat.-Sun. 10-18
Mon.-Fri. 9-20, Sat.-Sun. 10-18